|
Research interests:
GABA and glutamate are the most prevalent neurotransmitters in central nervous system (CNS), which mediate inhibitory and excitatory transmissions, respectively. Imbalance between inhibitory and excitatory transmissions has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various CNS diseases, including neuronal developmental disease (e.g. sex differentiation), epilepsy, and schizophrenia. On the other hand, the CNS neurons are often surrounded by astrocyte processes, in which transporters located on astrocyte membrane, play a pivotal role in the inactivation of GABAergic and glutamatergic neuronal transmissions. The astrocytic glutamine-glutamate cycle (see Figure 1 cartoon below) is a typical example of amino acids metabolic interaction between neurons and astrocytes that could modulate GABAergic and glutamatergic synaptic strengths during brain development and under brain diseases.
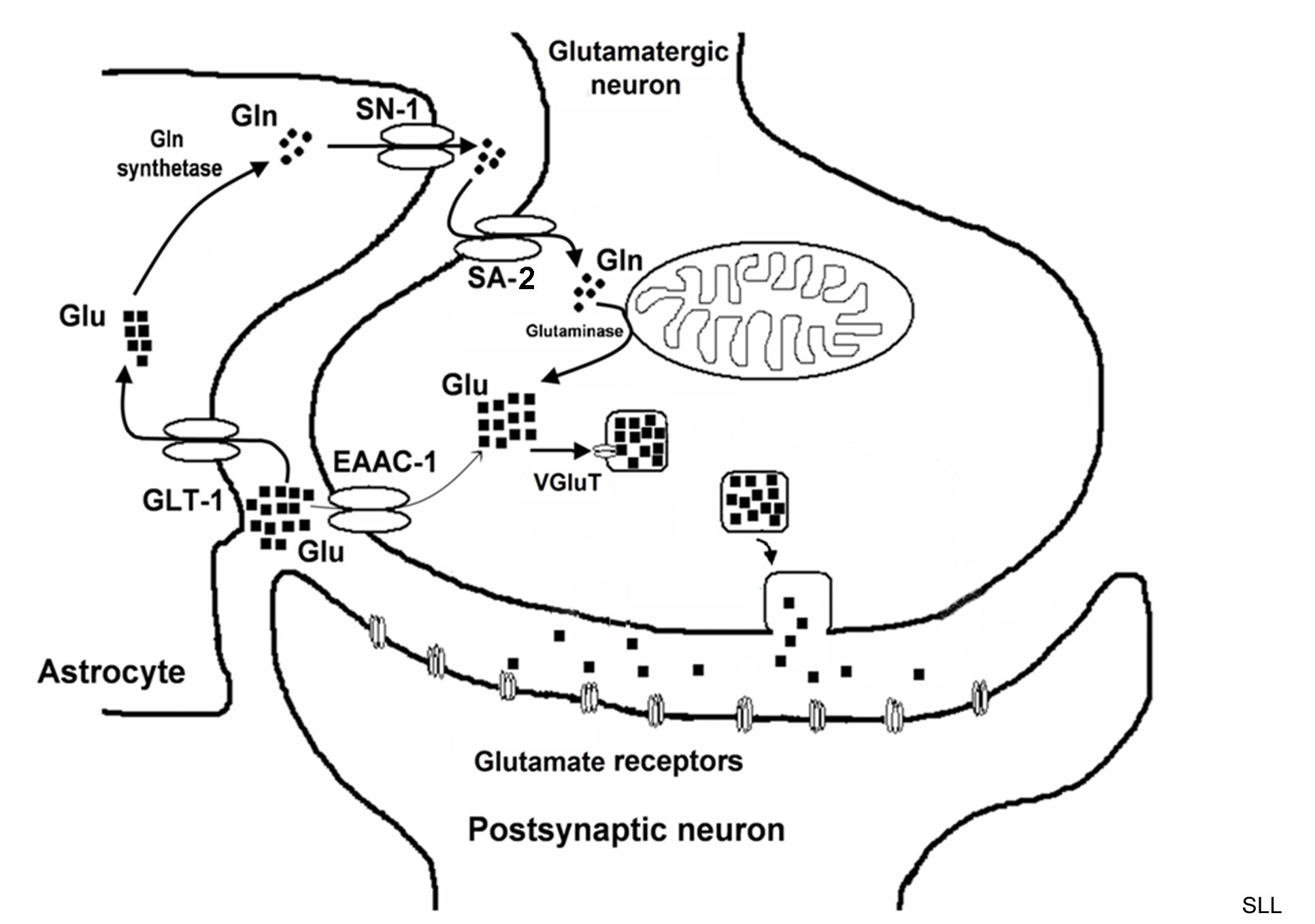
Figure 1. Vesicular neurotransmitter(s) originating from the glutamine - glutamate cycle may depend on astrocytic synthesis and transport. Illustrated are the three cellular components of a glutamatergic synapse: the pre- and post-synaptic elements, which are often surrounded by astrocytic processes. The primary transporters regulating presynaptic uptake of glutamate (Glu, n ; EAAC-1) is shown on the face of the synapse. The Glu-glutamine (Gln) cycle pathway is indicated by the thick arrows, starting with astrocytes uptake Glu through GLT-1, and convert Glu into Gln via glutamine synthetase (Gln, l). Gln can then be transported out through System-N transporters (SN-1) and into the neuron through System-A transporters (SA-2). Neurons use Gln to synthesize Glu via glutaminase. The Glu can then be packaged into the vesicle via vesicular Glu transporters (vGluT).
Use a variety of electrophysiology techniques in conjunction with pharmacological interventions, qualitative and quantitative mRNA and protein analysis as well as behavioral tests, three research topics are currently on going in my lab:
- Cellular mechanisms of the GGC on the regulation of glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmissions during brain sex differentiation in rats.
- Cellular mechanism of adenosine receptor subtypes in the regulation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission and feminized brain in the hypothalamic neurons of neonatal female rats
- Cellular mechanisms of the GGC in the regulation of GABAergic synaptic transmissions in temporal lobe epilepsy in rats.
Research approach:
- Adapting visualized whole-cell voltage and current clamp recordings techniques, inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs; EPSCs), firing activity used cell-attached technique are routinely used to examine the changes of synaptic functions, in which several parameters are used and listed below:
- Miniature IPSCs (mIPSCs), miniature EPSCs (mEPSCs) for testing changes in synaptic efficacy under basal condition of synaptic activities.
- Strontium evoked IPSCs and EPSCs; miniature evoked IPSCs (meIPSCs) and miniature evoked EPSCs (meEPSCs) for testing changes in potency and release probability under active synapses.
- Recording spontaneous IPSCs (sIPSCs), spontaneous EPSCs (sEPSCs), evoked IPSCs (eIPSCs), evoked EPSCs (eEPSCs) and field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) to assess synaptic efficacy.
- Paired-pulse stimulation recordings to determine changes in synaptic vesicle’s release probability.
- Puffed GABA or glutamate for testing changes in postsynaptic receptors’ numbers or sensitivity.
- Pair-recordings to directly assess synaptic interaction between pre- and post-synaptic neurons.
- Astrocytic GABA and glutamate transporter currents recordings to reflex extracellular GABA and glutamate concentration.
- Western blotting analysis for semi-quantification protein levels of interested proteins.
- Quantitative RT-PCR for evaluation RNA levels.
- Immunocytochemistry for post hoc analysis of recorded neuron.
- Animal behavior observation and identification, including reproductive behavioral tests
List of Publications (2018-present):
Journal Articles (peer-reviewed):
- Liang SL*, Chen RS (2024) The glutamine-glutamate cycle contributes to behavioral feminization of female rats. Neuroendocrinology (Submitted; *, corresponding author)
- Liang SL*, Liao WL, Chen RS (2023) Perinatal blockade of neuronal glutamine transport sex differentially alters glutamatergic synaptic transmission and organization of neurons in the ventrolateral ventral medial hypothalamus of adult rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 35: e13253 (*, corresponding author)
- Liang SL*, Tong YS, Hwang LL, Huang YZ, Chen CY (2022) CART peptides differently regulate firing rates and GABAergic synaptic inputs of DMV neurons innervating the stomach and cecum of adult male rats. Neuroendocrinology 112:555-570. (*, corresponding author).
- Liang SL (2018) The glutamate-glutamine cycle regulates synaptic glutamate release in ventrolateral ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus of perinatal female rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 30: e12642.
Published Abstracts:
- Liang SL, Chen RS: Metabolic interaction between astrocytes and neurons via the glutamine-glutamate cycle contributes to behavioral feminization of female Rats. The 37th Joint Annual Conference of Biomedical Science, Taiwan, Taipei, Mar 18-19, 2023. (PY050)
- Liang SL, Liao WL, Chen RS: Perinatal blockade of neuronal glutamine transport sex differentially alters glutamatergic synaptic transmission and organization of neurons in the ventrolateral ventral medial hypothalamus of adult rats. Taiwan Society for Neuroscience, Interdisciplinary Neuroscience Congress, Taiwan, Taoyuan, Sep. 2-4, 2022. (P2-30)
- Liang SL, Chen RS: Perinatal interruption of the glutamine-glutamate cycle (GGC) permanently compromises GGC-dependent basal excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmissions of hypothalamic neurons of female rats. The14th Meeting of the Asia Pacific Federation of Pharmacologists (APFP), Taiwan, Taipei, Nov 26-29, 2021. (H033)
- Lin YS, Liang SL: Blockade of neuronal glutamine uptake during brain development differently changes fertility of female rats. The 34th Joint Annual Conference of Biomedical Science, Taipei, Taiwan, Mar 23-24, 2019. (P061, enter the final poster contest held by The Chinese Physiological Society).
- Lin YS, Liang SL: Neonatal disruptions of the glutamate-glutamine cycle reduce the expression of sexual behavior and fertility of female rats. The 33th Joint Annual Conference of Biomedical Science, Taipei, Taiwan, Mar 24-25, 2018. (PY073).
Patent:
1. Liang, S.L. (2019) Use of glutamine in improving sexual dysfunction. Taiwan, ROC. Patent No. I652059.
Chinese Articles
- 簡介腦神經疾病與星狀膠細胞麩胺酸—麩胺醯胺循環異常的關連(2011, 十月),梁淑鈴,長庚醫訊:32卷10期,增刊第54-57頁。
- 凡德氏人體生理學(Vander’s Human Physiology,2023,Sep.),第16版,梁淑鈴等合譯,潘震澤總校閱,合記圖書出版社,台灣,台北市。
Honors and Awards:
- Lin YS, Liang SL: Neonatal disruptions of the glutamate-glutamine cycle reduce the expression of sexual behavior and fertility of female rats. Second place in the Master thesis contest held by Graduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences of Chang Gung University, Taiwan, Tauyuan, Jul 2-6, 2018. (2C09).
- Lin YS, Liang SL: Neonatal disruptions of the glutamate-glutamine cycle reduce the expression of sexual behavior and fertility of female rats. Third place in the poster contest held by The Chinese Physiological Society in the 33th Joint Annual Conference of Biomedical Science, Taiwan, Taipei, Mar 24-25, 2018. (PY073).
- Tong YS, Hwang LL, Chen CY, Liang SL: Different regulations of CART peptides on firing rates and synaptic inputs of DMV neurons innervating stomach and cecum in rats. Third place in the poster contest held by The Chinese Physiological Society in the 32th Joint Annual Conference of Biomedical Science, Taiwan, Taipei, Mar 25-26, 2017. (PY060).
- The Marsden Fund Referee, The Marsden Fund is affiliated by New Zealand Government and is administered by the Royal Society of New Zealand. 2014.
- Editorial Board Member in Journal “Animal Cells and Systems”, The Official Journal of the Korean Society for Integrative Biology. 2010~2013.
- National Science Council Outstanding Researcher Award, 2011.
|



